Electrosurgery is commonly used for cutting, coagulating, dissecting, electrocautery, ablating and shrinking tissue in ophthalmic surgery. High frequency (100 kHz to 5 MHz), various voltage (200-10,000 volts) alternating current generates heat through the tissue. An electrosurgical unit (ESU) consists of a generator and a mobile phone with one or more electrodes. The device is controlled using a switch on the phone or a foot switch. The electrosurgical generator can generate a variety of electrical waveforms. As these waveforms change, the corresponding tissue effects will also change.
Did you know that electrosurgery is used in over 80% of all human surgical procedures? With well-established benefits for human procedures, this proven technology is now being adopted more and more by animal health professionals around the world.
Monopolar Electrosurgery
The effectiveness and versatility of monopolar electrosurgery make it the most commonly used option. This type of electrosurgery provides a variety of electrosurgical waveforms with different tissue effects. In monopolar electrosurgery, pencil electrodes are used to cut target tissue and/or coagulate bleeding. Use the return electrode pad and connect it to the patient and safely recover the energy passing through the body.
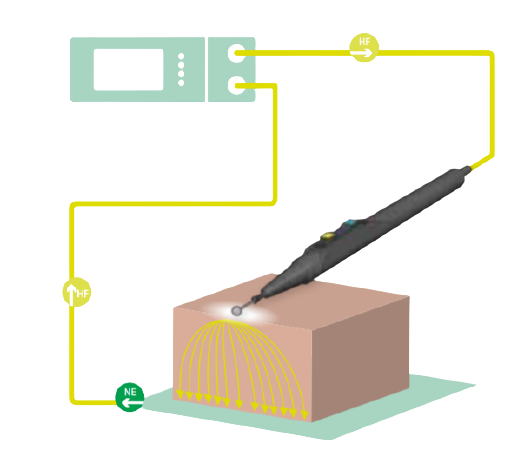
Bipolar Electrosurgery
Bipolar electrosurgery provides more concentrated energy for very specific tissue areas. In addition, bipolar electrosurgery significantly reduces the risk of burns in patients. This method is very suitable for specific operations such as ear trimming and other operations that allow easy access to both sides of the tissue. The use of bipolar technology does not require a return pad because the current only passes through the tissue, not the patient’s entire body. Whether you choose a bipolar method or a unipolar method, electrosurgery is a more effective method to maximize the effect. The benefits far exceed traditional methods.


Tissue Heating
As electrical current enters tissue, the ions within the cells become excited and
begin to go into motion, releasing kinetic energy. As this action increases or is
prolonged, the cells begin to heat.
The temperature rise in tissue is directly proportional to:
• the resistance of the tissue
• the current density
• the power output
• the time of current application

